PRP for Hair Restoration: A Modern Solution for Hair Loss
Hair loss affects millions worldwide, impacting confidence and self-esteem. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy has emerged as a promising, non-surgical treatment for hair restoration. Here is a little info on what PRP is, how it works for hair loss, its benefits, and what to expect from the procedure.
Hair loss affects millions worldwide, impacting confidence and self-esteem. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy has emerged as a promising, non-surgical treatment for hair restoration. Here is a little info on what PRP is, how it works for hair loss, its benefits, and what to expect from the procedure.
What is PRP Therapy?
PRP therapy involves using a patient’s own blood to promote healing and tissue regeneration. Blood is drawn and processed in a centrifuge to concentrate platelets, which are rich in growth factors. These growth factors stimulate cell repair, collagen production, and tissue regeneration. In hair restoration, PRP is injected into the scalp to rejuvenate hair follicles and encourage hair growth.
How Does PRP Work for Hair Restoration?
PRP targets hair follicles that are dormant or weakened but still viable. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Blood Collection: A small amount of blood (similar to a routine blood test) is drawn from the patient.
- Centrifugation: The blood is spun in a centrifuge to separate the platelet-rich plasma from other blood components.
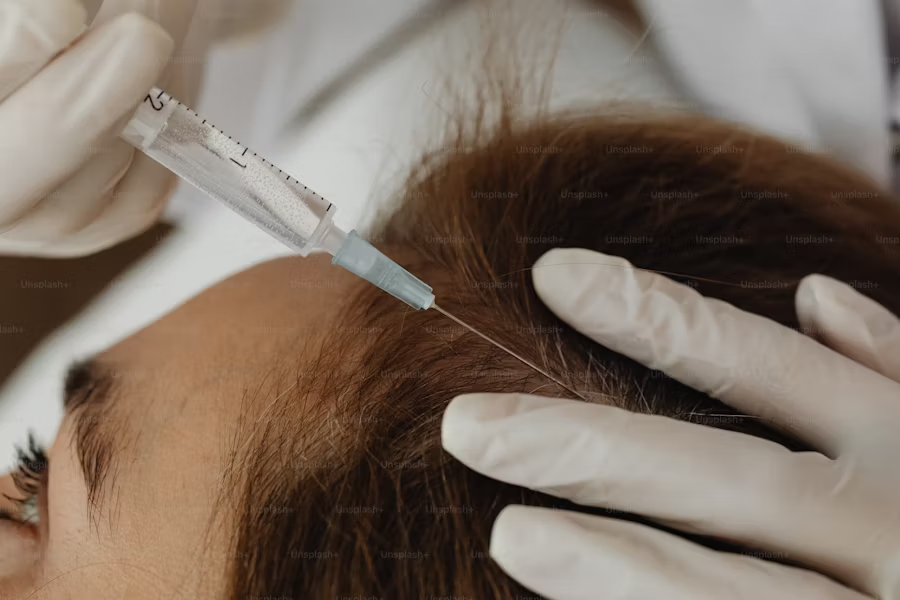
- Injection: The concentrated PRP is injected into areas of the scalp with thinning hair or hair loss using fine needles.
- Stimulation: Growth factors in PRP stimulate dormant hair follicles, improve blood supply, and promote thicker, healthier hair growth.
The procedure is minimally invasive, typically lasting 60–90 minutes, and requires little to no downtime.
Benefits of PRP for Hair Restoration
PRP therapy offers several advantages for those seeking to address hair loss:
- Non-Surgical: Unlike hair transplants, PRP is non-invasive, making it a low-risk option.
- Natural Treatment: Since PRP uses the patient’s own blood, there’s minimal risk of allergic reactions or side effects.
- Improved Hair Quality: PRP can enhance hair thickness, density, and overall scalp health.
- Versatile: It’s effective for various types of hair loss, including androgenetic alopecia (male/female pattern baldness) and alopecia areata.
- Quick Recovery: Patients can resume normal activities immediately after treatment.
Who is a Good Candidate for PRP?
PRP is best suited for individuals in the early stages of hair loss or those with thinning hair. It’s less effective for completely bald areas where hair follicles are no longer present. Ideal candidates include:
- Men and women with mild to moderate hair thinning.
- Individuals seeking a non-surgical alternative to hair transplants.
- Those with realistic expectations about gradual hair improvement.
A consultation with a dermatologist or hair restoration specialist can determine if PRP is appropriate based on the extent of hair loss and overall health.
What to Expect During and After PRP Treatment
During the Procedure
- The scalp is cleaned, and a numbing cream may be applied to minimize discomfort.
- PRP injections are administered using small needles, which may cause mild stinging or pressure.
- The session typically takes about an hour, depending on the treatment area.
After the Procedure
- Mild redness, swelling, or soreness at the injection sites may occur but usually subsides within a day or two.
- Patients can wash their hair the next day and resume normal activities immediately.
- Multiple sessions (3–6, spaced 4–6 weeks apart) are often recommended for optimal results, followed by maintenance treatments every 6–12 months.
Results
Hair growth is gradual, with noticeable improvements typically seen after 3–6 months. Results vary based on individual factors like age, genetics, and the extent of hair loss. Combining PRP with other treatments, such as minoxidil or low-level laser therapy, may enhance outcomes.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
PRP is generally safe due to its autologous nature (using the patient’s own blood). However, minor side effects may include:
- Temporary scalp tenderness or swelling.
- Mild bruising at injection sites.
- Rarely, infection or nerve irritation if not performed by a qualified professional.
Choosing a licensed and experienced provider is crucial to minimize risks and ensure proper technique.
PRP vs. Other Hair Loss Treatments
Compared to other options, PRP stands out for its natural approach and minimal invasiveness:
- Minoxidil/Finasteride: Topical or oral medications require daily use and may cause side effects like scalp irritation or hormonal changes. PRP is a procedure with no ongoing maintenance between sessions.
- Hair Transplants: Surgical transplants offer permanent results but involve higher costs, longer recovery, and potential scarring. PRP is a less invasive alternative or complement to transplants.
- Laser Therapy: Low-level laser therapy stimulates hair follicles but may take longer to show results. PRP often delivers faster improvements.
The Future of PRP for Hair Restoration
Ongoing research continues to refine PRP protocols, such as optimizing platelet concentration and combining PRP with stem cell therapy or exosomes for enhanced results. As technology advances, PRP may become even more effective and accessible for hair loss sufferers.
Conclusion
PRP therapy offers a safe, natural, and effective solution for hair restoration, particularly for those in the early stages of hair loss. With minimal downtime and a low-risk profile, it’s an appealing option for men and women seeking to regain thicker, healthier hair. If you’re considering PRP, consult a qualified specialist to discuss your goals and determine if this innovative treatment is right for you.
Ready to take the next step? Schedule a consultation with Dr. Leticia to explore how PRP can help you achieve fuller, more vibrant hair.